What is Electroconvulsive Therapy?
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) is a medical treatment that involves sending brief electric currents to the brain, keeping the patient under general anesthesia. The whole process is operated by professional medical persons who have previous experience of doing this.
It is used to stimulate the brain and change the brain chemistry to reverse or change the symptoms of some mental health conditions. ECT is mainly used to treat people with major depression and bipolar disorder who have already gone through other treatment processes but the situation hasn’t changed.
In ECT, a very weak electric signal is passed to the brain. Still, there were some side effects of it. With time, the tools and instruments have been improved, also the process. So, now the rate of side effects is very low, though those are still there.
How Does Electroconvulsive Therapy work?
In Electroconvulsive Therapy, small electric currents are sent to the brain. Those cause a seizure. Researchers haven’t found yet how the electric currents work to alter the symptoms of depression.
It is supposed that these small electric current flows affect the chemicals that are responsible for transferring messages between the nerve cells. As a result of that, some type of biochemical change happens and thus the symptoms of mental disorders disappear.
The treatment process of ECT typically requires the patient to stay in the hospital. But nowadays, it is being transformed into an outpatient treatment session.
This is a 5-10 minute process but the preparation for it takes some time. At first, the patient is kept sleeping using anesthesia. An anesthesiologist pushes the particular amount of anesthetic in vain. Also, in some cases, a muscle relaxant is used. During the process, the supply of oxygen is given through a face mask. Blood pressure and oxygen level are always monitored continuously.
After the anesthesia is in action, small electrodes are placed on the scalp or/and temple. Then, small electric currents are passed between the electrodes through the brain. This current flow stimulates the brain and causes a controlled seizure that lasts for around 20 to 90 seconds.
This controlled seizure doesn’t cause any movement of the body. After a few minutes, the patients wake up from sleep without any memory of the treatment. Thus the whole process of ECT takes place under a controlled and continuously monitored the situation in a medical facility.
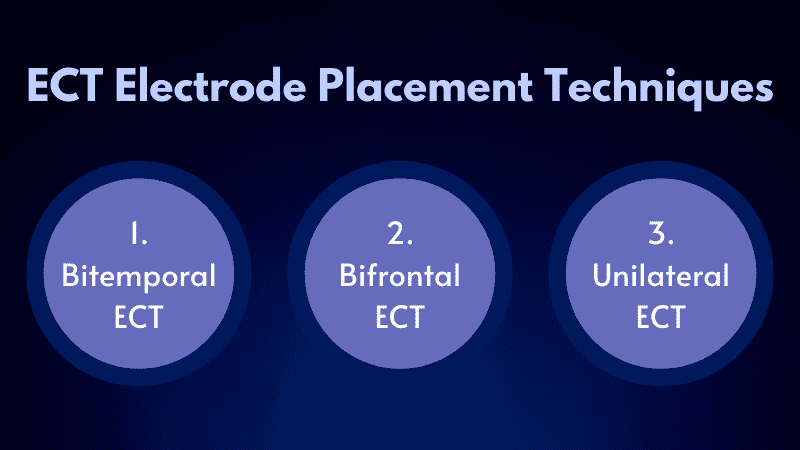
ECT Electrode Placement Techniques
Electroconvulsive Therapy includes the placement of electrodes near the brain of the patients. Depending on the point where to set the electrodes, ECT is divided into some common types. These are-
1. Bitemporal ECT
In the Bitemporal system, the therapist draws an imaginary line from the tragus to the external canthus. The electrodes are placed just 1-inch above the midpoint of this imaginary line.
2. Bifrontal ECT
In Bifrontal ECT, the electrodes are placed by drawing an imaginary line from the tragus to the external canthus, just like the Bitemporal method. But in this one, the electrodes are placed more frontal compared to the Bitemporal system.
3. Unilateral ECT
In this system, one electrode is placed on the non-dominant frontotemporal area. As in most people, the left hemisphere is dominant. So, in most cases, it is placed on the right hemisphere. Another electrode is placed on the side of the midline vertex of that non-dominant area.
These are the most common placements of electrodes in ECT therapy. There are many other methods with their pros and cons. But, typically, it doesn’t have any huge impact on the impact. Some studies have been done to find the actual dissimilarities. But to come to a perfect conclusion, many more studies and research are needed.

What is Electroconvulsive Therapy Used for?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is used to treat severe symptoms of some mental health issues. This is an effective therapy that has the ability to bring quick and significant improvement in mental health conditions.
Below are the main mental health issues that can be treated with ECT.
1. Severe Depression- When the symptoms of depression are very serious and the patient starts thinking of committing suicide, stops eating, or becomes completely unaware of reality.
2. Catatonia- Catatonia is a condition in which the patient shows a lack of speech, lack of movement, strange movement behaviors, and strange activities. Catatonia can be caused by medical illness. But in most cases, it is the result of schizophrenia or some other similar mental illness.
3. Severe Mania- This is a state of hyperactivity, agitation, or euphoria caused by bipolar disorder. When it reaches a severe situation, ECT can reduce the symptoms. Other symptoms of it are substance abuse, impulsive behavior, psychosis, etc.
4. Several Symptoms of Dementia- ECT is used to treat some severe symptoms of dementia, including aggression or agitation.
Typically ECT is used when medication or other psychotherapies don’t bring any changes. In such cases, there is no other way except ECT. Also, there are some other situations where ECT is used. Below are the situations when ECT is used-
- During pregnancy. Medications can harm or create an impact on the development of the fetus. So, instead of medication, ECT is used.
- Older adults may not handle the impact or side effects of medications. In this case, ECT is used.
- Sometimes, the patients prefer ECT over medications. In such cases, ECT is used on them.
- ECT is used to treat a patient who has gone through ECT in past and found a good result from it.
How Long Does Electroconvulsive Therapy Last?
If you ask about the length of a single Electroconvulsive Therapy session, the answer is about 1 hour. This 1 hour includes the preparation for the therapy, time spent in the treatment room, and time spent in the recovery room.
Preparing the treatment room may take around 10 minutes. Then the patient is taken to the room. The process in the treatment room lasts for around 15-20 minutes. It includes pushing the anesthesia, sending electric signals through the brain, and waking up from sleep.
After the treatment room, the patient is taken to the recovery room. A typical duration spent in the recovery room is 25-30 minutes. So, overall, a single session of ECT takes around 1 hour.
The whole treatment process of ECT requires around 9 to 15 sessions. The number of sessions may vary depending on the condition of the patient.
Unlike psychotherapy processes, ECT suggests arranging sessions twice or thrice a week. So, the overall length of treatment with ECT is around 1 or 2 months.
ECT is used to treat severe mental health conditions. So, there is no scope of taking a long time like psychotherapy treatments.
How much does Electroconvulsive Therapy Cost?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is a costly therapy if you consider the cost of each session as it includes anesthesia and medical arrangement in each session. Let’s see the typical cost of ECT.
Each session of ECT charges around $300 to $1000 depending on where the treatment process is taking place. Some therapists or facilities charge even more amount, depending on the amenities of the treatment room and recovery room, the expertise of the therapist, and so many other factors.
This charge excludes additional stay in the hospital if required.
Let’s pick the average cost per session is $700 and the average number of sessions required as 10. So, a patient has to spend around $7000 for the sessions. Sometimes, throughout the year, the patient has to receive around 10-15 maintenance sessions. So, an additional $7000-$10000 per year will be added to the cost.
But there are some ways of getting the cost reduced. For example- discounts, sliding scale technique, insurance, etc. But for reducing the cost, don’t go to a beginner therapist for such types of sessions. Go to the experts who can do it properly.
ECT is cost-effective. It brings the expected benefits in most cases. In around 60-80% of cases, the patients have been benefited from the treatment. The percentage of recovering is higher than the percentage of psychotherapy approaches. So, though you have to spend a good amount of money on it, the benefits you’ll receive are worth the expenditure.
Is Electroconvulsive Therapy Safe?
Electroconvulsive Therapy is a great treatment option for people with mental health issues that medicine can’t cure. But as it includes the process of passing electricity through the brain, there is a question- is it safe?
The answer to the question is- yes, it is safe.
In maximum ECT treatments, the patients haven’t faced any long-term issues. Maximum have finished the process with zero issues when some have faced some short-term side effects.
The main reason it is safe is that the electric current passed in the ECT therapy is very short and low power. This is enough for a bit of change in the brain chemistry. But this can’t cause huge issues like brain damage, or other problems that people face after getting an electric shock.
Also, with the advance of technology, the ECT process is continuously being developed. So, it is possible to control the process without facing any issues. The tools used in ECT are much performance-focused and action-specific. This ensures the efficiency and safety of the treatment process.
So, you can say that ECT is comparatively safe though it may cause some side effects.
Below are the side effects that can happen after ECT.

What are the Side Effects of Electroconvulsive Therapy?
As electric signals are sent to the brain, ECT has some side effects. Using science and technology, the therapy and the process is being improved gradually. But side effects happen sometimes. Some of those are short-term some are long-term.
Below are some of the side effects of ECT.
1. Drowsiness- After the therapy, the patients may feel drowsiness for some time. Also, the patients may sleep for a few hours after the therapy session.
2. Confusion- Typically older adults face confusion after ECT. They may not recognize where they are or why they are there. Confusion lasts for a few minutes or a few hours. In worst cases, it may stay for several days.
3. Headache- This is another common side effect of ECT. Headache typically stays for a few hours. A proper rest removes the headache.
4. Muscle Ache- This is not common but sometimes the patients may feel muscle ache after an ECT session. It needs a few hours or a day to leave.
5. Memory Loss- Memory loss is another side effect caused by ECT. In most cases, the memory loss is for a short time. After a while, the memories come back. But in some cases, the issue is not so easy. Long-lasting and permanent memory loss may happen too.
In some cases, people forget their important life events or memories. Sometimes, they forget information related to their job and career. Also, the ability to memorize something decreases a lot sometimes.
It is suggested to perform memory and thinking ability tests before and after treatment of ECT.
6. Medical Issues- Medical issues are common after any medical treatment that uses anesthesia. So, ECT may cause some medical issues too. During ECT, an increase in blood pressure and heart rate is seen. In rare cases, it leads to major heart problems. So, patients who have heart problems are typically not encouraged to take ECT treatment.
7. Loss of drive, energy, and creativity- As ECT changes the brain chemistry a bit, it affects the creativity of a person. Also, it can reduce the mental drive and energy towards something.
8. Difficulty in Concentration- After ECT, in some cases, the patients start losing their power of concentration. They face difficulties in concentrating on something.
These are some risk factors of ECT. In most cases, there is not any long-term impact. Rarely, but in some cases, the impacts are long-term. So, before proceeding with ECT, the patients and family members should keep these in mind.

Electroconvulsive Therapy Pros and Cons
As Electroconvulsive Therapy is an effective therapy for some mental issues where medication and other therapies don’t work, it can be counted as one of the most useful therapies to treat such issues. However, still, there are some cons too. Let’s know the pros and cons of ECT.
Pros of ECT
- ECT is a great tool as it can fix the issue quickly. In some cases, 1-2 sessions are enough to reach the expectation, though the typical average is 8-10 sessions.
- In most cases, ECT doesn’t need any medicine alternation.
- In cases where the patient can’t take medications because of the side effects, ECT is helpful because it doesn’t have side effects that medications typically have.
- For depression, ECT is the best-known treatment process. In researches, it is seen that the effectiveness rate of ECT is around 60%-80%, which is better than any therapies or medications.
- For Catatonia, ECT is a well-known and the most effective treatment. The effectiveness, in this case, is around 90% which is much more than any type of psychotherapy.
- The ECT process is advancing day by day. Hopefully, someday it will be more controllable and the side effects can be removed completely.
Cons of ECT
- ECT is a bit costly, though insurance covers it.
- People with weak hearts can’t tolerate ECT.
- Comes with the risk of side effects though most of those are short-term.
- ECT contains the minor complexities caused by anesthesia.
- Driving is forbidden up to a few weeks after treatment.
- Old people may not tolerate ECT in many cases.
These are the pros and cons of ECT. In the case of ECT, you’ll find that the pros and cons are almost similar in number. So, it is a bit difficult to make the decision.
But the cons of ECT are mostly condition-based. For example- if you’re not old or a heart patient, two cons disappear. Again, the complexities caused by anesthesia are common in treatments that include anesthesia. ECT has nothing to do with it.
Thus most of the cons can be avoided. So, typically we suggest going for it. Still, there are risks. So, the decision is always yours.
Electroconvulsive Therapy for Depression
It is called that the best treatment for depression is Electroconvulsive Therapy. When any medication or psychotherapy can’t cure depression, ECT can. But how does ECT do it?
There is no specific answer to the question because the scientists and researchers haven’t found any specific answer yet. Through multiple types of research, it is seen that ECT has effectively treated most of the patients who were suffering from severe depression.
After receiving ECT therapy, most of the patients have gone back to their regular life or started to respond to medications or other psychotherapy approaches. Also, the rate of committing suicide is very low in the patients who have taken ECT treatment.
But, exactly how ECT treats depression is not known yet. It is thought that the electric current passed through the brain stimulates the chemicals that pass messages to the cell. Also, some say that ECT helps to release dopamine and serotonin.
Both of these hormones are known as happy chemicals because they are responsible for transmitting happiness. According to them, the production of happy chemicals makes the patient feel happy and avoid stress. Thus, ECT removes depression or reduces its severity.
This is an acceptable answer to the question about how ECT treats depression.
To treat depression, ECT typically requires 6 to 10 sessions. If the severity is high, 10-12 sessions are typically enough. The improvement in the condition is seen after the first 2 To 3 sessions.
Electroconvulsive Therapy for Schizophrenia
Like depression, Electroconvulsive Therapy works great on schizophrenia. But when the question is about how it does it, the answer is uncertain.
It is supposed that ECT works to treat schizophrenia exactly as it treats depression. The release of hormones like dopamine and serotonin has an impact on the situation of patients with schizophrenia.
If we see the common reasons behind schizophrenia, we’ll find that stress, sadness, and relationship problems are some of the reasons behind it. Also, schizophrenic patients tend to be sad and hopeless maximum the time.
Happy chemicals like serotonin and dopamine lift the mood of the patients. Thus, ECT makes the patient happy and as a result of it, schizophrenia is reduced to some extent.
Studies have proven the effectiveness of ECT on schizophrenia many times. A study by Lin et al. in 2018 has shown that people who are treated with ECT for schizophrenia have been less hospitalized for psychiatric problems after the treatment compared to the people who aren’t treated with ECT. The use of antipsychotics with ECT becomes more effective.
There are some other studies that have shown the effectiveness of ECT on schizophrenia. But still, the number of studies is inadequate and more researches are needed to find out how ECT impacts patients with schizophrenia.

Myths about ECT
There are a lot of myths you’ll hear about Electroconvulsive Therapy. Those don’t have any authenticity and are not spread depending on the facts. Let’s know some myths about ECT and the facts.
Myth 1- ECT is a barbaric treatment
Fact: ECT is called barbaric because electric shock is used in this therapy. But the fact is, the electric current passed in ECT is very brief. So, there is no chance of any huge problem. Also, before passing the current, the patients are given anesthesia. So, they don’t even feel that they are given an electric shock.
ECT is a fully controlled process where the patients don’t feel anything when the current is passed. So, you can’t call it barbaric activity.
Myth 2- ECT causes brain damage
Fact: ECT never causes brain damage. Instead, it helps the brain to improve its performance.
According to a brain donor study, it is seen that after giving ECT treatment, there is no change in the brain cells. Many other studies have shown that, instead of damaging cells, it increases Dopamine, Serotonin, Norepinephrine, and some other chemicals that cause happiness and mood lift-up.
Recent researches also have shown that ECT increases the hormones that generate, grow, and heal damaged nerve cells.
Myth 3- ECT causes permanent memory loss
Fact: Memory loss is a side-effect of ECT but it is not permanent. In most cases, the memory loss lasts for a few hours. In some cases, this might be prolonged to a few days. Permanent or long-term memory loss is very rare.
Treatment time, additional medications, etc. may reduce the side effect to an extent. Also, the latest ECT technology has reduced the risk a lot.
Still, before taking the therapy, the patients are informed of the side effects. The decision solely depends on the patient.
Myth 4- ECT is dangerous
Fact: This myth has also spread as ECT includes electric current flow through the brain. But the fact is, it is not dangerous at all. The current is very brief. Also, the process is conducted by qualified medical persons under expert supervision. So, it is a safe therapy.
Myth 5- ECT is only for depression
Fact: ECT treats depression effectively, it is true. But this is not only for depression. As ECT helps the brain to release happy chemicals that lift the mood, this can be a great treatment option for mood-related disorders. Also, it shows a great result in treating Catatonia. In this case, ECT is around 90% effective.
Myth 6- ECT cures depression
Fact: ECT works great where medication or other therapies don’t work. For this reason, sometimes it is considered as the cure for depression. But ECT is not a cure.
The fact is- mental health issues can’t be cured fully. These can be treated and the symptoms can be kept under control. ECT is an effective treatment that can keep the symptoms under control. In some cases, after the primary sessions of ECT, the patient can stay well for a long time. Depending on those cases, people think that ECT is a cure.
But in most cases, to stay well, ECT sessions should be continued on a regular basis to boost the effectiveness.
Myth 7- ECT is the last resort
Fact: Typically ECT is used when no other treatment can work. The reason is- because of the misconception and side effects, most of the patients don’t want to receive the treatment in the primary stages. They try other ways at first. When there is no other way, they try ECT.
As a result, a myth has been spread that ECT is the last phase of treatment. But the act is, in some cases, this can be used at the very first phase to get effective results.
These are some of the common myths about ECT. There are misconceptions and a lack of research. So, people don’t know much about it. That’s why the myths have been created.
But the fact is- it has some side effects that people can be afraid of, but ECT is a great therapy technique that ensures impressive results. The myths and rumors shouldn’t stop the progress of such an effective treatment.

Frequently Asked Questions about ECT
Below are some of the frequently asked questions about ECT. Check these if you have any more questions.
What if any side effect happens?
Answer- The patients are monitored after each session of ECT. The monitoring process checks for two things- the response to the session and the presence of any side effect. If there is any symptom of serious side effects, the sessions are discontinued.
As a result, if there any side effect tends to happen, it is understood at the initial stages. Depending on the issue, the doctors take the necessary steps for avoiding it.
Is it possible to go through ECT more than once?
Answer- It depends on the situation.
If your first treatment using ECT goes well and improves the situation, ECT can be considered again as a treatment process for some other mental health conditions.
However, if your previous ECT treatment can’t show any improvement, typically ECT is not used again. The doctor may suggest ECT in such cases only if all other treatment opportunities are explored and those can’t show any improvement.
Can doctors treat patients using ECT if they don’t consent to it?
Answer- In general cases, without consent, the doctors can’t treat any patient with ECT. Before the decision, the doctors should inform the patients about the risks, side effects, and other important information. After listening to all of these, if the patients decide to go through ECT, the therapy is provided.
But when there is no consent from the patient, ECT can’t be used. But there are a few exceptional situations where consent of the patient is not needed. These are-
- When the patient is not in a condition of giving consent
- When the patient requires emergency mental treatment under the Mental Health Act
Final Verdict
This is almost all about Electroconvulsive Therapy. In this brief article, I’ve tried to discuss ECT in short. There are many more things to know about it. I’ve talked about what ECT is, how it works, the problems it treats, and many more. I’ve also talked about some common myths about it and the facts.
I guess, this article can help you to know the basics about ECT. This is a huge area that can’t be discussed fully in this brief article. If you’re interested, you can go through other available resources on the internet.